Retinopathy
Retina and diabetes:
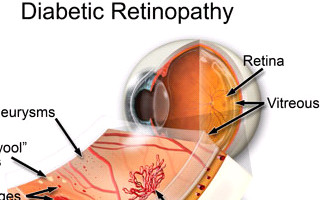
The retina is like a camera photographic film. In fact, it is a photosensitive tunic (membrane) in eye fundus which is able to convert visual stimuli into optical information sent to the brain.
Undoubtedly, diabetes is a disorder that frequently occurs at all ages, Its main characteristic is high levels of glucose (sugar) in the human body. Diabetes is able to affect even eyesight, causing a dangerous condition called diabetic retinopathy.
What exactly is diabetic retinopathy?
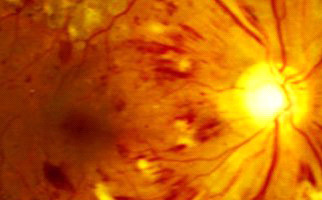
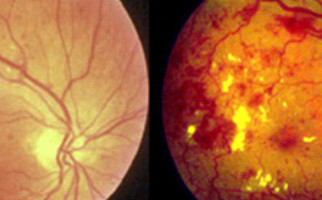
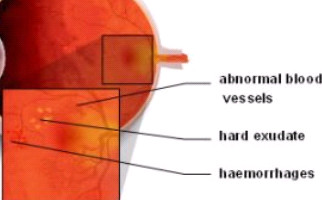
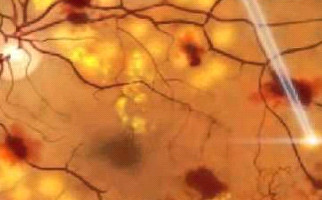
Diabetic retinopathy is indeed an extremely serious complication in ophthalmic fundus, due to diabetes. More specifically, the condition destroys and changes the retina vessels. Those vessels’ serious damages result in hemorrhages, tissue necrosis and neovessels formation. The probability someone to present the condition depends on how long he / she suffers from diabetes. Nowadays, due to juvenile diabetes, diabetic retinopathy occurs also in young people and it is considered as one of the most serious reasons for vision loss worldwide. Diabetic individuals should regularly monitor their blood sugar levels.
Symptoms:
The truth is that diabetic retinopathy is considered as an insidious disease. Even with the severe eye fundus damages, the patient may not realize the seriousness of the situation. However, some of the symptoms are the following:
- Vision fluctuations (visual acuity changes)
- Small shadows in visual fields
- Double vision (diplopia)
- Significant delay during healing (e.g. after a corneal trauma)
There are two diabetic retinopathy forms (stages):
-Background retinopathy: It is the early – warning stage (sign) of the condition. Small retinal capillaries are damaged, causing serous fluid leakage or hemorrhage. This results in oedema formation (retinal thickening) and formation of exudates. When fluid is concentrated on macular region, vision is influenced and the condition is known as diabetic macular edema.
-Proliferative retinopathy: It is caused by extensive retinal vascular obstruction that contributes to reduced perfusion of photoreceptors. Under these conditions, the retina reacts by developing neovessels for blood production (oxygen) at ischemic areas. Neovessels are insufficient for perfusion, thus a number of extra issues occur. One major issue is retinal detachment condition.
Treatment:
The only certainty is that diabetic patients should monitor sugar levels and keep necessary medication, in case it is administered.
Laser applications (photocoagulation): This technique’s primary goal is to stabilize vision. Laser beams are focused on damaged retina in order to seal the retinal vessels leaking and reduce the macular edema (abnormal neovascular growth). Repeated laser shots prevent abnormal vessel growth (detachment avoidance).
Cryotherapy: In case the vitreous presents blood opacities, laser photocoagulation is not the best solution. After blood clearance, the ophthalmologist uses cryotherapy technique (freezing retina). The method is in position to catalytically assist in reducing the number of abnormal vessels.
Vitrectomy: It is purely a surgical procedure and is used in the advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy (proliferative retinopathy). The surgeon removes the cloudy vitreous humor and replaces it with a clean solution. Vitrectomy method is used also in retinal detachment cases.