Macular degeneration
What exactly is the macula?
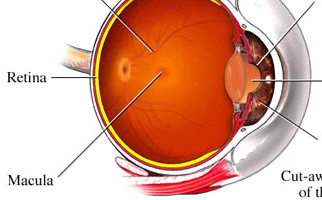
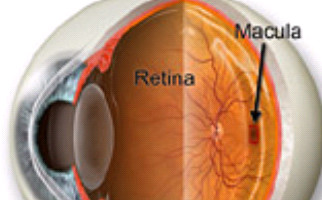
In fact, macula is the central part of the retinal layer (ocular fundus). It is responsible not only for central vision, but also allows us to see details with clarity (e.g. while reading), so named because of its yellowish appearance. When macula’s functionality is affected, we receive dark or distorted stimuli in our central vision.
What exactly is the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and which are its main causes?
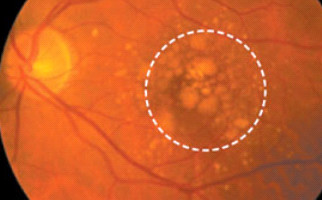
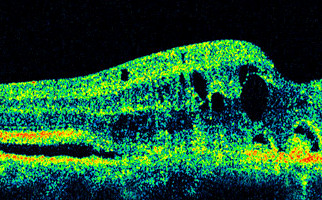
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a chronic ophthalmic condition that occurs with aging, basically in individuals over 60. Without doubt, it is one of the most dangerous reasons for vision loss worldwide. Elderly people have AMD, as result of normal aging. At the early stages of the disorder, some substance depositions, called Drusen, are observed underneath the retina. They can be visible (diagnosed) during an eye fundus ophthalmological examination. Much of the time Drusen do not lead to serious vision loss. But at the advanced stages of AMD, negative vision effect is tremendous (e.g. visual acuity may be less than 2/10). AMD occurrence risk factors are: age, smoking, obesity, heredity and sunlight exposure. The main symptoms are metamorphopsia (distorted vision), contrast sensitivity deterioration and gradual visual acuity decrease.
AMD forms:
-Dry AMD (non-exudative or non-neovascular): most common form and less dangerous (85-90% of cases), slowly progressive. Macular atrophy, aging and thinning are the main reasons for dry AMD. The main symptoms are scotomas in central vision field.
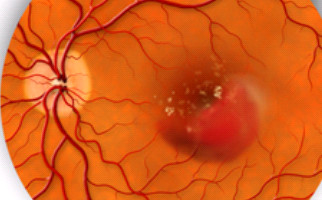
-Wet AMD (exudative): Although rare (10-15% of cases), undoubtedly one of the leading causes for severe vision loss. Abnormal pathological vessels (neovessels) grow on the retinal layer, underneath the macula (choroidal neovascularization). Neovessels leak serous fluid and blood, destroying the photosensitive macular cells and this situation leads to central vision loss.
Dry AMD treatment:
- Healthy / balanced diet with nutritional supplements (vitamins C, E, minerals, zinc) slow up the progression of the condition
- Drastic smoking reduction
- Arterial blood pressure regulation
- Sports & gymnastics
Wet AMD treatment:
-Laser photocoagulation: High intensity laser pulses help prevent pathological neovessels development. Because of the heat, developed by the laser, neovessels are burned and destroyed. This specific technique is used when neovessels are not underneath the central section of the macula.
-Photodynamic treatment (PDT): With this method, a substance called Verteporfin (Visudyne) is administered intravenously. Verteporfin has the ability to be selectively withheld by the abnormal (pathological) neovessels. The main advantage of PDT technique, in comparison to photocoagulation laser is that PDT laser is less intense (no heat, no thermal damage). PDT laser activates Visudyne substance, which then selectively occludes pathological neovessels, without affecting the surrounding healthy retinal tissue. This treatment is usually performed every 3 months.
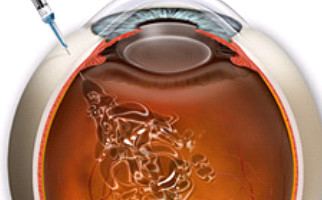
–Intravitreal injections (ANTI-VEGF injections): This is a different therapeutic approach (latest development in wet AMD treatment). A number of injections are made in the eye in order to inject a special drug which inhibits VEGF factor (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor). In fact, VEGF factor favors the development of pathological neovessels. Treatment for blocking VEGF factor is so called ANTI-VEGF technique (intravitreous injections) and the most prevalent drugs used nowadays are Lucentis (Ranibijumab) and Avastin (Bevacijumab). The entire procedure is short and completely painless. It takes place in a sterile surgical room and requires no hospitalization. Sometimes the technique is combined with PDT laser.
-Surgical procedure: Wet form AMD can be treated via surgery by removing the neovascular membrane or by displacing macula from the neovascularization area.