Cataract
What exactly is cataract and which are its causes?
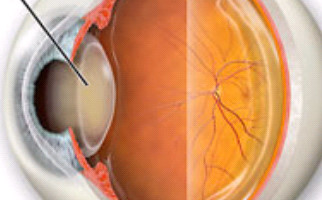
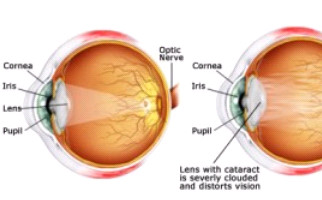
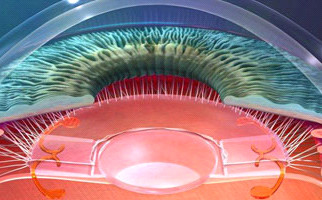
Progressive, with aging, clouding of the natural, crystalline lens (behind iris) of the eye, is called a cataract. This ophthalmic condition appears usually over 55, but occurs also in younger ages, due to eye injuries or metabolism disorders. Congenital cataract makes its appearance at birth but it is quite rare. Exposure to sunlight (ultraviolet radiation) and poor diet accelerate the condition’s occurrence.
Symptoms:
The main cataract symptoms are the following:
- Opaque, blurry, dark or reduced vision
- Regular changes in eye-spectacles prescriptions
- Faded colors (reduced color perception)
- Glares, distracting reflections, halos, light sensitivity, photophobia
- Negative effect on contrast sensitivity
- Significantly reduced night vision
Treatment:
Cataract, in early stages, can be faced with eye spectacles, but this definitely a temporary solution. The complete cataract extraction is performed with a surgical procedure, known as phacoemulsification with ultrasound. This technique is a high-lever surgery. Among the continuous technological innovations, cataract surgery (phacoemulsification) has been considered and established as a routine procedure with 98% success rate.
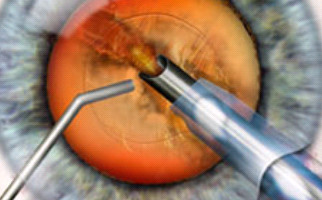
Phacoemulsification
Phacoemulsification technique of is the most widespread solution for cataract removal worldwide. It is quick and almost painless. Initially, anesthetic drops are instilled and 2 tiny incisions are created in the eye (2 – 3 mm), in order to create the capsulorhexis, a circular opening in the anterior capsule for a special tool (as small needle) insertion, emitting ultrasound so as to shatter and absorb the cloudy lens. In natural lens capsule, an artificial lens is properly placed, called intraocular lens (IOL). Phacoemulsification method is absolutely safe and does not contain sutures. It is not necessary for phaco-patient to stay in a clinic after surgery. Patients are able to immediately return to their daily activities. Cataract surgery can be combined with presbyopia and astigmatism treatments.
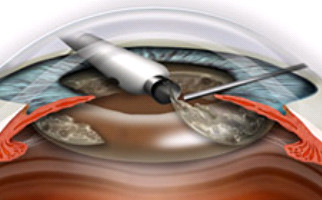
Intraocular lens (IOL)
In fact, an intraocular lens is an artificial retractable lens (acrylic or silicone) which is implanted (injected) in the eye, during phacoemulsification surgical procedure and replaces the cloudy cataractous lens.
IOL types:
-Monofocal IOL: one focal point for qualitative distant vision
-Monofocal toric IOL: one focal point for qualitative distant vision and corneal astigmatism correction
-Multifocal IOL: multiple focal points for qualitative near, intermediate and distant vision (presbyopia treatment)
-Multifocal toric IOL: multiple focal points for qualitative near, intermediate and distant vision (presbyopia treatment) and combinatorial corneal astigmatism correction
-Adaptive IOL: offers eye’s natural lens adaptation for qualitative vision at all distances
What is secondary cataract?
Capsule is a thin membrane that accommodates the natural lens of the eye. After cataract surgery (emulsification) and IOL implantation, posterior capsule blurring is possible. This condition is called secondary cataract. Gradually reduced vision is one of its symptoms and it makes its appearance in 8 to 10% of people who have undergone cataract surgery. Treatment takes place even in a simple infirmary with the help of capsulotomy technique, using a special laser system, called yag laser.